Fatty Liver: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
Last updated on : 21 Apr, 2025
Read time : 8 min
What is fatty liver disease?
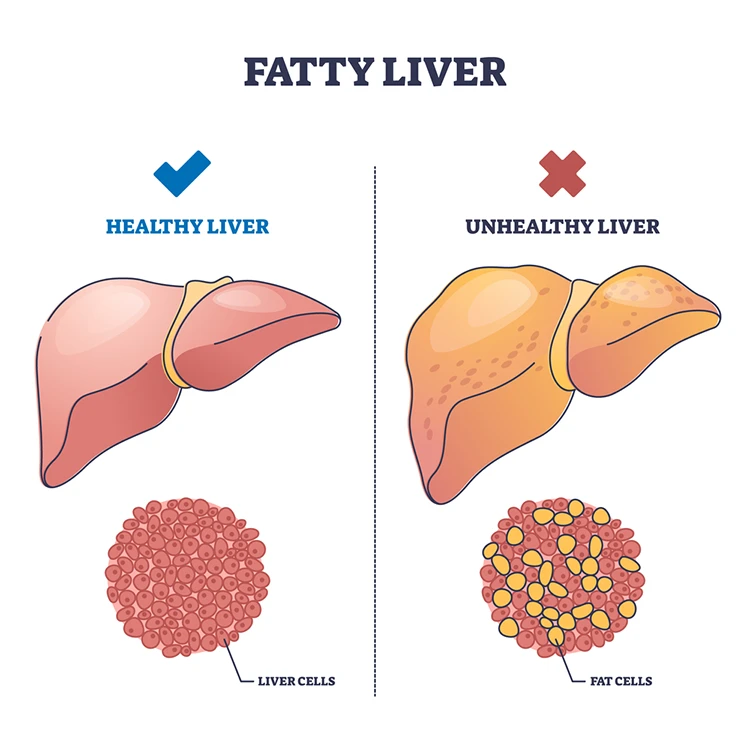
It is a condition that is characterised by fat build-up inside the liver. The liver is the largest organ inside the human body. It helps in the digestion process, energy storage and removal of toxins from the body.
Fatty liver disease can happens because of things like drinking too much alcohol, being overweight, or having certain health conditions. It’s essential to take care of your liver by eating healthy and avoiding things that can harm it, like too much alcohol.
Fatty Liver Disease Symptoms
Fatty liver symptoms can vary and might not show at first. But as the condition worsens, you might feel tired, weak, or have pain in the upper right part of your belly. You might also notice swelling in your belly or legs, or have yellowish skin or eyes. Some people with fatty liver disease might lose weight or feel nauseous. If you have any of these symptoms, it’s essential to see a doctor for a checkup and get proper treatment. Early detection and management can help prevent complications.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
There are two types of fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or alcoholic steatohepatitis
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterised by fat in the liver with or without inflammation and with or without liver damage. Additionally, it may lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer, especially in steatohepatitis (a type of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease)
Alcoholic fatty liver disease
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is mainly due to alcohol consumption. The alcohol consumed is metabolised in the liver, removes the metabolised products, and releases toxic substances that are harmful to the liver. The toxins cause inflammation and weaken the defence system of the body. The more the consumption of alcohol, the more significant the damage to the liver.
Differences between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease is mainly due to excess consumption of alcohol, which leads to liver cancer. At the same time, Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is not due to alcohol consumption.
- Diabetes, pre-diabetes, high blood pressure, high levels of cholesterol and overweight issues are the leading causes of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. At the same time, only alcohol consumption is the cause of alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- The treatment for alcoholic fatty liver diseases is the reduction of alcohol consumption. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment includes lifestyle changes, i.e. reducing weight in case of being overweight, eating a balanced diet and reducing unnecessary medications and alcohol.
- The fatty degeneration of liver cells is faster in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease than in alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Similarities between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic fatty liver disease
- The risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease are very similar. They include people with pre-diabetes and type -2 diabetes, obesity, middle-aged people (children also get it sometimes), high levels of fats in the blood like cholesterol and triglycerides, high blood pressures, use of corticosteroids and other anti-cancer drugs, people with metabolic disorders including metabolic syndrome, have rapid weight loss, have infections like hepatitis C, and exposed to some toxic substances.
- The symptoms of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic fatty liver disease are not prominent or are silent most of the time. If you feel you have a few symptoms, such as pain in the upper right side of your stomach, discomfort and tired feeling,
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease both have fat accumulated inside the liver.
- Both are severe types of health problems worldwide.
- Alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease are common signs of disease progression from simple liver steatosis to steatohepatitis, liver cirrhosis and then liver cancer.
- Differentiation of both diseases is difficult.
- The diagnosis of both alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease includes taking a medical history, physical examination, and tests to diagnose alcoholic/non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. The medical history includes being overweight, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol levels in the blood and metabolic syndrome. Physical examination includes an enlarged liver and dark patches on elbows and knees, indicating insulin resistance and cirrhosis. Tests include imaging tests like ultrasound, CT Scan, and MRI Scan.
Fatty Liver Disease Treatment
You can try a few things that will help in the management of fatty liver treatment. This includes:
- Lose weight: The first step for fatty liver treatment usually involves losing weight. It helps to reduce fat, inflammation, and scarring in your liver. Just losing a little bit of weight, like up to 5% of your body weight, can lower the amount of fat in your liver. If you need to lose a lot of weight, weight loss surgery could be an option too.
- Quit alcohol: You also have to stop drinking alcohol. It’s the only way to stop your liver damage from getting worse. You might even be able to make some of the liver damage go away. Talk to your doctor about how they can help you. You might need a special program to stop drinking and deal with any withdrawal symptoms safely.
- Vitamin E: Research suggests that vitamin E might help liver health by lessening inflammation, but the effects can differ based on factors like the amount taken, the person’s age, and how overweight they are. However, some studies warn that taking too much vitamin E could be risky for people with certain medical conditions, including fatty liver disease.
- Medications: To manage diabetes, cholesterol, and triglycerides (fat in the blood), make sure to take the medicines prescribed by your doctor and refer to the list of foods to avoid with high triglycerides. This will indirectly help in the management of fatty liver disease.
Conclusion
Fatty livers are of two types. Alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver. Both fatty livers are due to the excess fat accumulation in the liver. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is due to excessive alcohol consumption. In contrast, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is due to other factors like pre-diabetes, type 2 diabetes, being overweight, high cholesterol levels in the blood, and high blood pressure. Both types have many similarities, which make it difficult to differentiate. However, diagnosis makes it possible to differentiate alcoholic fatty liver disease from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Yes, fatty liver can be treated and managed with lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
Fatty liver disease can be serious if left untreated, as it can progress to more severe liver conditions like cirrhosis or liver failure.
The time it takes for fatty liver to heal varies depending on factors such as the individual’s overall health, the severity of the condition, and adherence to treatment. It can take weeks to months or longer to see improvement.
Foods that are good for liver repair include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, and avocados. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding processed foods and excessive alcohol consumption can also support liver health.
Foods that support liver repair include fruits like berries and citrus fruits, vegetables like leafy greens and cruciferous vegetables, whole grains like oats and quinoa, lean proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu, and healthy fats like those found in nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Additionally, drinking plenty of water and avoiding processed foods and excessive alcohol consumption can help promote liver repair.
References
- Toshikuni N, Tsutsumi M, Arisawa T. Clinical differences between alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol [Internet]. 2014 [cited 2023 July 23];20(26):8393–406. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8393
- [cited 2023 July 23]. Available from: http://ttps://medlineplus.gov/fattyliverdisease.html
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) & NASH [Internet]. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. [cited 2023 July 23]. Available from: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash
Disclaimer
Our healthcare experts have carefully reviewed and compiled the information presented here to ensure accuracy and trustworthiness. It is important to note that this information serves as a general overview of the topic and is for informational purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, prevent, or cure any health problem. This page does not establish a doctor-patient relationship, nor does it replace the advice or consultation of a registered medical practitioner. We recommend seeking guidance from your registered medical practitioner for any questions or concerns regarding your medical condition.
Popular Articles
Recommended Articles
Recent Articles
Top-Selling Medicines:
...View more
Top-Selling OTC:
...View more
Company
About UsHealth ArticleHealth StoriesDiseases & Health ConditionsAll MedicinesAll BrandsNeed HelpFAQSubscribe
Registered Office Address
Grievance Officer
Download Truemeds

Contact Us
Our customer representative team is available 7 days a week from 9 am - 9 pm.
v3.7.12
Our Payment Partners



























































